About window.postMessage()
The window.postMessage() method safely enables cross-origin communication. Normally, scripts on different pages are allowed to access each other if and only if the pages that executed them are at locations with the same protocol(https). window.postMessage() provides a controlled mechanism to circumvent this restriction in a way which is secure when properly used.
How it works:
when called, causes a *MessageEvent to be dispatched at the target window when any pending script that must be executed completes (e.g., remaining event handlers if window.postMessage() is called from an event handler, previously-set pending timeouts, etc.)
The MessageEvent has the type message, a data property which is set to the value of the first argument provided to window.postMessage(), an origin property corresponding to the origin of the main document in the window calling window.postMessage at the time window.postMessage() was called, and a source property which is the window from which window.postMessage() is called. (Other standard properties of events are present with their expected values.)
Demo of window.postMessage()
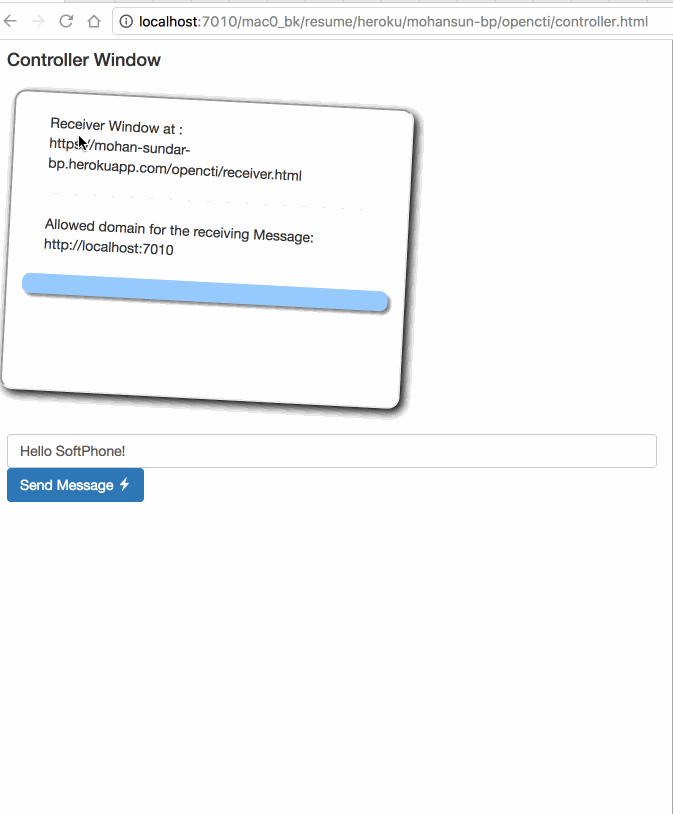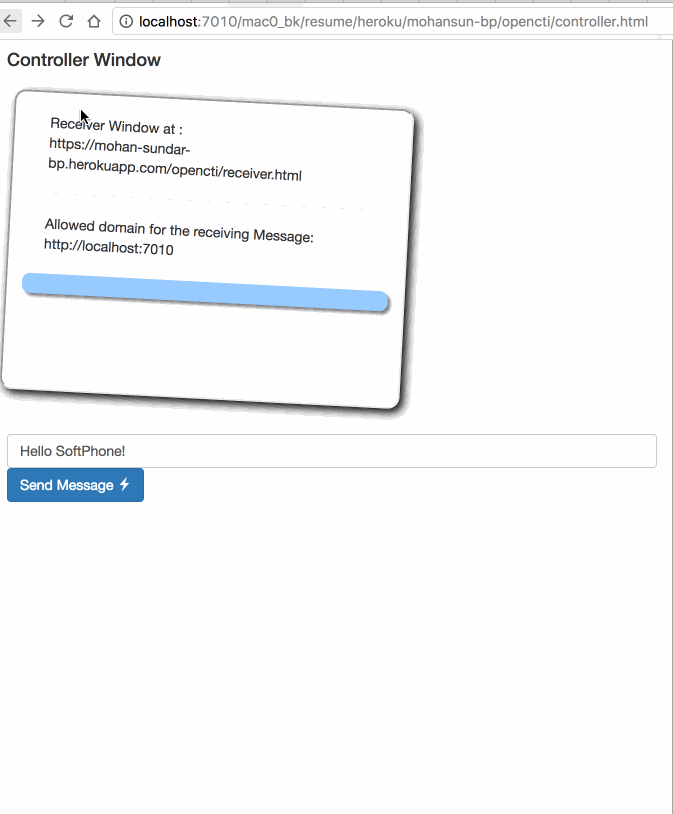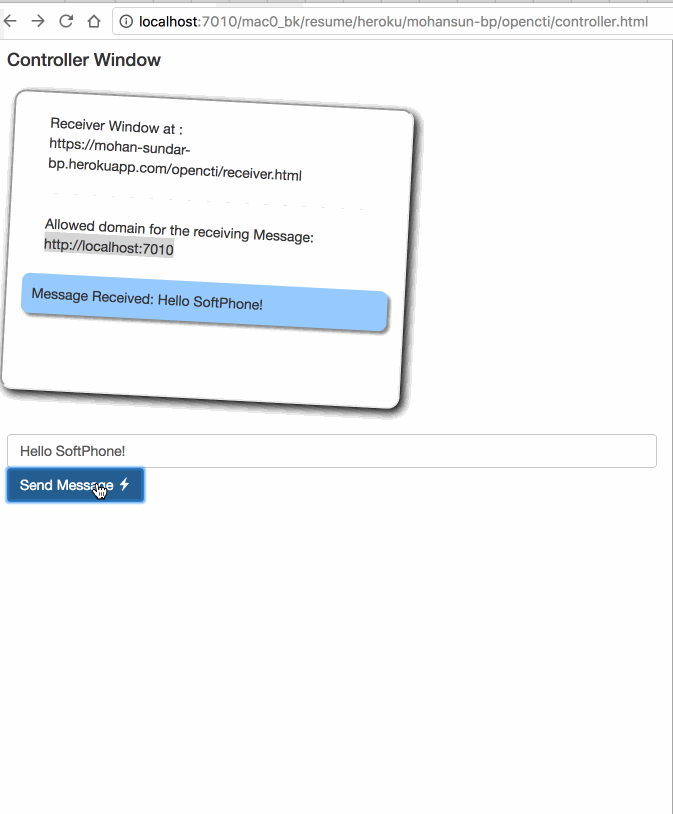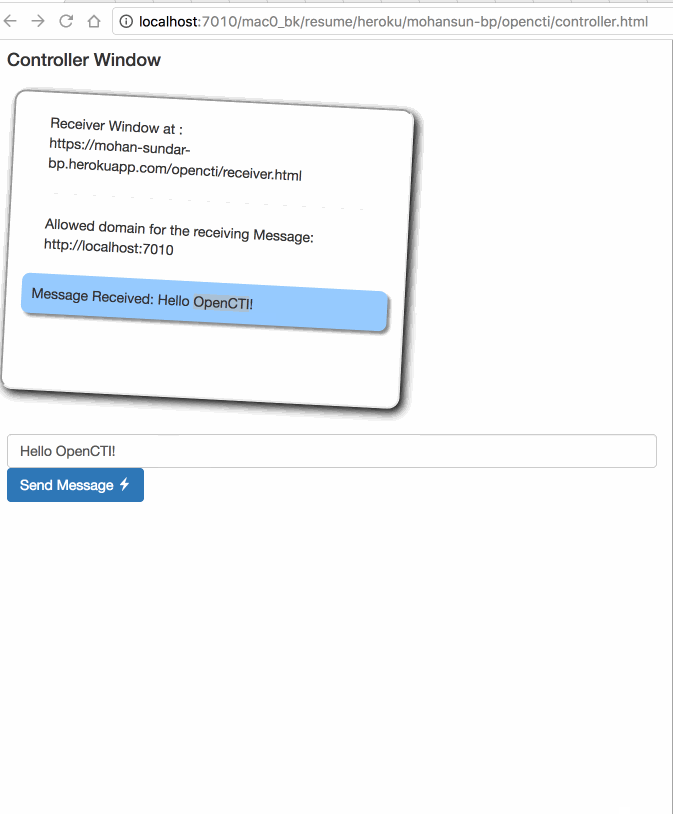
window.postMessage
